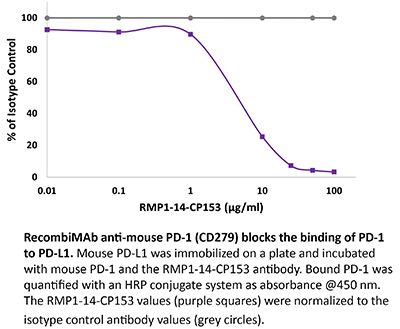
RecombiMAb anti-mouse PD-1 (CD279) (LALA-PG)
| Clone | RMP1-14-CP153 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Catalog # | CP153 | ||||||||||||
| Category | in vivo Recombinant Antibodies | ||||||||||||
| Price |
|
The RMP1-14-CP153 monoclonal antibody is a chimeric version of the original RMP1-14 antibody. The variable domain sequences are identical to the original RMP1-14 but the constant region sequences have been switched from rat IgG2a to mouse IgG2a. The RMP1-14-CP153 antibody also contains a LALA-PG mutation in the Fc fragment rendering it unable to bind to endogenous Fcγ receptors. RMP1-14-CP153 reacts with mouse PD-1 (programmed death-1) also known as CD279. PD-1 is a 50-55 kDa cell surface receptor encoded by the Pdcd1 gene that belongs to the CD28 family of the Ig superfamily. PD-1 is transiently expressed on CD4 and CD8 thymocytes as well as activated T and B lymphocytes and myeloid cells. PD-1 expression declines after successful elimination of antigen. Additionally, Pdcd1 mRNA is expressed in developing B lymphocytes during the pro-B-cell stage. PD-1’s structure includes a ITIM (immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motif) suggesting that PD-1 negatively regulates TCR signals. PD-1 signals via binding its two ligands, PD-L1 and PD-L2 both members of the B7 family. Upon ligand binding, PD-1 signaling inhibits T-cell activation, leading to reduced proliferation, cytokine production, and T-cell death. Additionally, PD-1 is known to play key roles in peripheral tolerance and prevention of autoimmune disease in mice as PD-1 knockout animals show dilated cardiomyopathy, splenomegaly, and loss of peripheral tolerance. Induced PD-L1 expression is common in many tumors including squamous cell carcinoma, colon adenocarcinoma, and breast adenocarcinoma. PD-L1 overexpression results in increased resistance of tumor cells to CD8 T cell mediated lysis. In mouse models of melanoma, tumor growth can be transiently arrested via treatment with antibodies which block the interaction between PD-L1 and its receptor PD-1. For these reasons anti-PD-1 mediated immunotherapies are currently being explored as cancer treatments.
See the references for the original rat IgG2a RMP1-14 antibody (https://bioxcell.com/invivoplus-anti-mouse-pd-1-cd279-bp0146).
| Isotype | Mouse IgG2a, κ |
|---|---|
| Recommended Isotype Control(s) | RecombiMAb mouse IgG2a (D265A) isotype control, anti-hen egg lysozyme |
| Recommended Dilution Buffer | InVivoPure pH 7.0 Dilution Buffer |
| Mutations | L234A, L235A, P329G (LALA-PG) |
| Immunogen | Syrian Hamster BKH cells transfected with mouse PD-1 cDNA |
| Reported Applications | in vivo blocking of PD-1/PD-L signaling* *Reported for the original rat IgG2a RMP1-14 antibody |
| Formulation | PBS, pH 7.0 Contains no stabilizers or preservatives |
| Endotoxin | <1EU/mg (<0.001EU/μg) Determined by LAL gel clotting assay |
| Aggregation | <5% Determined by DLS |
| Purity | >95% Determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Sterility | 0.2 µm filtration |
| Production | Purified from CHO cell supernatant in an animal free facility |
| Purification | Protein G |
| Molecular Weight | 150 kDa |
| Murine Pathogen Tests | Ectromelia/Mousepox Virus: Negative Hantavirus: Negative K Virus: Negative Lactate Dehydrogenase-Elevating Virus: Negative Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis virus: Negative Mouse Adenovirus: Negative Mouse Cytomegalovirus: Negative Mouse Hepatitis Virus: Negative Mouse Minute Virus: Negative Mouse Norovirus: Negative Mouse Parvovirus: Negative Mouse Rotavirus: Negative Mycoplasma Pulmonis: Negative Pneumonia Virus of Mice: Negative Polyoma Virus: Negative Reovirus Screen: Negative Sendai Virus: Negative Theiler’s Murine Encephalomyelitis: Negative |
| Storage | The antibody solution should be stored at the stock concentration at 4°C. Do not freeze. |